欢迎在文章下方评论,建议用电脑看
状态集合S: 有限状态state集合,s表示某个特定状态
动作集合A: 有限动作action集合,a表示某个特定动作
状态转换分布(state transition distribution)。对于每个属于集合S的状态s和每个属于集合A的动作a,如果我们在状态s中采取了动作s,那么我们就会转换到一个新的状态中,而状态转换分布就给出了我们会随机转换到哪个状态的概率分布。
 分布(state transition distribution)。对于每个属于集合S的状态s和每个属于集合A的动作a,如果我们在状态s中采取了动作s,那么我们就会转换到一个新的状态中,而状态转换分布就给出了我们会随机转换到哪个状态的概率分布。
分布(state transition distribution)。对于每个属于集合S的状态s和每个属于集合A的动作a,如果我们在状态s中采取了动作s,那么我们就会转换到一个新的状态中,而状态转换分布就给出了我们会随机转换到哪个状态的概率分布。
也就是在某个状态采取某个动作之后的一些转换概率

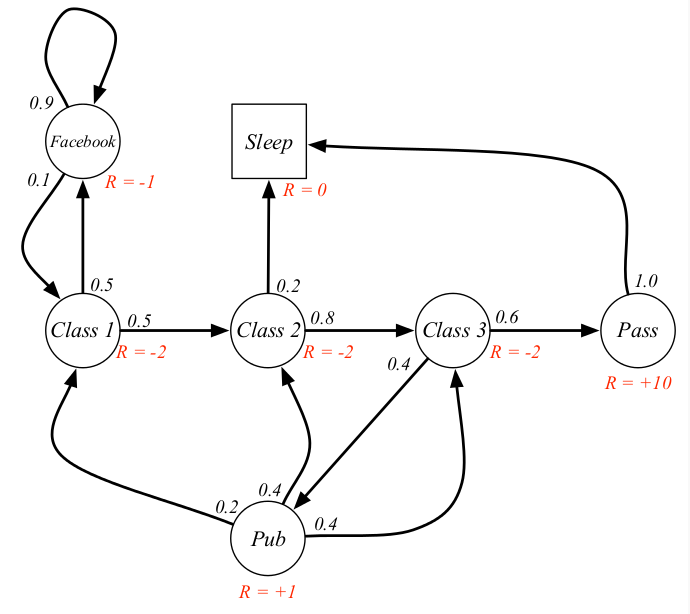
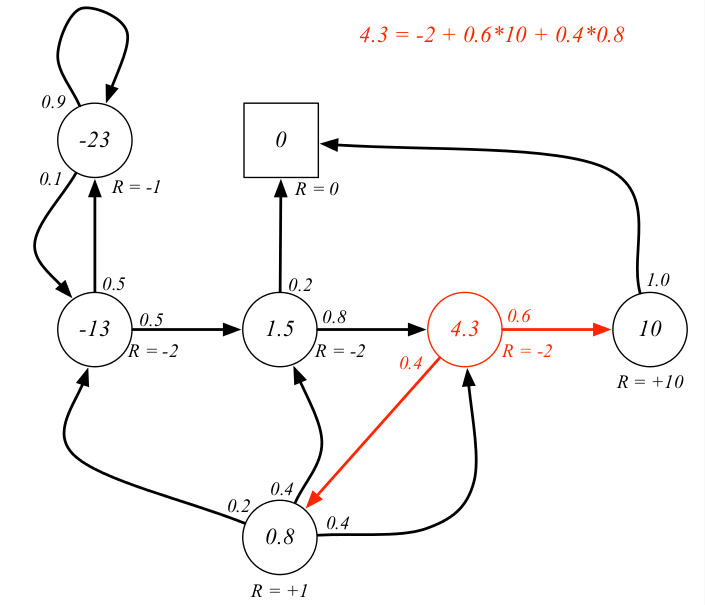
从MP开始到MRP再到MDP,了解值函数的具体概念与reward有什么联系
MDP描述了强化学习的environment,且是fully Observable的
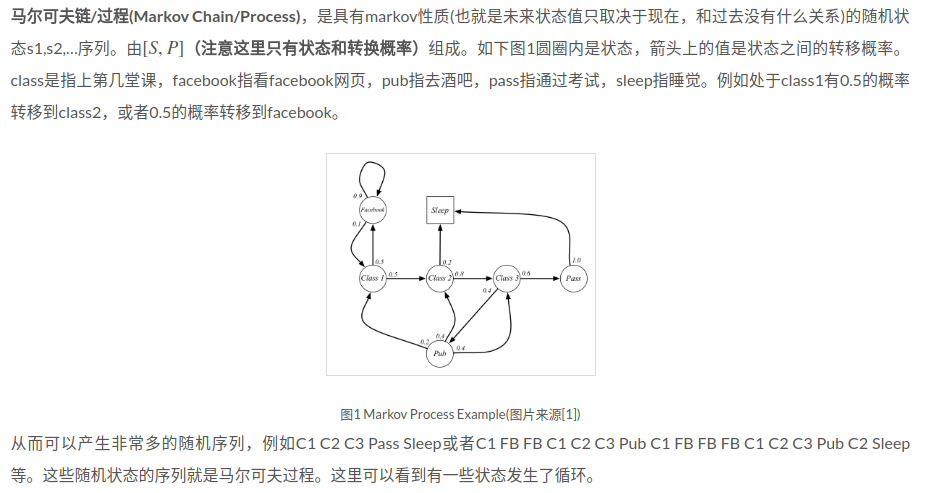
先说说马尔可夫性质:“The future is independent of the past given the present”
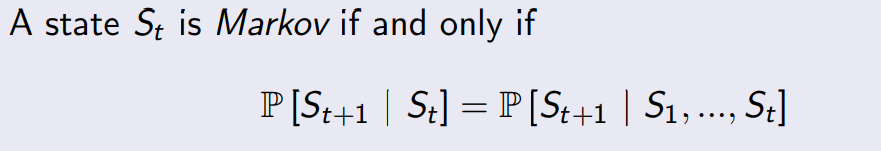
The state captures all relevant information from the history,Once the state is known, the history may be thrown away。i.e. The state is a sufficient statistic of the future
课件原文:
For a Markov state s and successor state s‘, the state transition probability is defined by
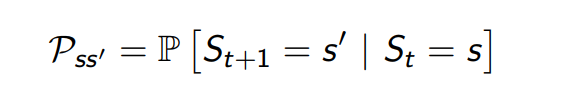
State transition matrix P defines transition probabilities from all states s to all successor states s’:
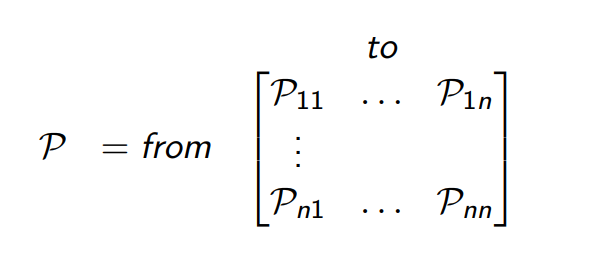
where each row of the matrix sums to 1
A Markov process is a memoryless random process, i.e. a sequence of random states S1, S2, … with the Markov property
A Markov Process (or Markov Chain) is a tuple <S,P> where S is a (finite) set of states and P is a state transition probability matrix, P(ss’) = P [S(t+1) = s’| S(t)= s]